RBG 1000

Low-concentration solid particle aerosols produced from powders are required for many research, development, and quality assurance applications and for calibrating particle measurement devices.
For more than 25 years, the RBG system has been used worldwide with great success for the reliable dispersion of non-cohesive powders such as mineral dusts, active pharmaceutical ingredients, pollen, etc., in size range of < 100 µm and with a fine fraction of < 100 nm. Also, monolithic solid materials such as blackboard chalk are finely dispersed with the highest dosing constancy.
The unique advantage of this dosing and dispersion system is that in the case of the RBG 1000, mass flows ranging from approx. 10 mg/h up to approx. 430 g/h are dispersed with the highest level of dosing constancy.
Optional:
- Pressure-resistant up to 3 bar
- Low-pressure operation from 300 mbar (absolute pressure), operation with nitrogen
Variants
More alternatives
Operation principle
Proven technology
The powder to be dispersed is put little by little into the cylindrical solid material reservoir and compressed with a tamper. In the context of the validation of the guideline "Prüfverfahren für mobile Raumluftreinigungsgeräte" at the Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts, an excellent reproducibility of the tamping density in the solid material reservoir was determined. The deviation of the tamping densities of five fillings was just 3.4 %.
The filled solid material reservoir is inserted into the dispersing head of the RBG, and the powder, which has thus been uniformly compressed across the filling level, is conveyed onto a rotating brush at a precisely controlled feed rate. An adjustable volume flow streams over the tightly woven precision brush at a very high speed and blows the particles out of the brush.
The entire material delivered can optionally be determined gravimetrically with the RBG 1000 L.
The dispersing head assembly comprises a dispersing head, dispersing cover, precision brush, and solid material reservoir.
Fig. 1: Schematic diagram of RBG system
Dosing is performed via the precisely controlled feed rate of the feed piston. The desired mass flows can be quickly and reproducibly specified based on the cross-section of the solid material reservoir, the precisely adjustable feed rate of the feed piston, and the easy-to-determine tamping density of the powder in the reservoir.
Mass flows of RBG 1000 / 2000 (compacted density 1 g/cm³)
| Reservoir diameter | Fill quantity | Feed rate 1 mm/h | Feed rate10 mm/h | Feed rate 100 mm/h | Feed rate 700 mm/h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 mm (RBG 1000) | 2.7 g | 38 mg/h | 380 mg/h | 3.8 g/h | 26.6 g/h |
| 10 mm (RBG 1000) | 5.5 g | 78 mg/h | 780 mg/h | 7.8 g/h | 54.6 g/h |
| 14 mm (RBG 1000) | 17 g | 150 mg/h | 1.5 g/h | 15 g/h | 105 g/h |
| 16 mm (RBG 2000) | 30 g | 200 mg/h | 2 g/h | 20 g/h | 140 g/h |
| 20 mm (RBG 1000) | 35 g | 310 mg/h | 3.1 g/h | 31 g/h | 217 g/h |
| 28 mm (RBG 1000) | 49.2 g | 616 mg/h | 6.16 g/h | 61.6 g/h | 430 g/h |
| 32 mm (RBG 2000) | 88 g | 800 mg/h | 8 g/h | 80 g/h | 560 g/h |
Table 1: Mass flows of RBG system (compacted density 1 g/cm3)
The filling height of the solid material reservoir is 70 mm.
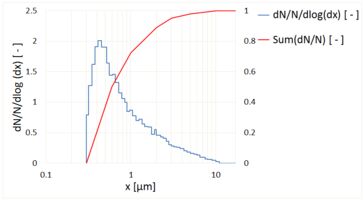
The powder separated from the reservoir by the precision brush is almost wholly dispersed into the constituent particles, down to < 100 nm (see Fig. 2), in the dispersing head by the dispersing air flowing at high speed.
Fig. 2: Particle size distribution with the welas® digital 2000
Fig. 3: Dispersing covers, type A, Type B and Type C
Four different dispersing covers can be used for optimal dispersion (see Fig. 3, additional details under "Accessories").
Dispersion covers RBG system
| Cover | Particle size | Reservoir diameter | Volume flow |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | < 0.1 – 200 µm | 7 – 32 mm | 33 – 80 l/min |
| B | < 0.1 – 200 µm | 7, 10 and 14 mm | 17 – 40 l/min |
| C | < 0.1 – 200 µm | 7 mm | 8 – 20 l/min |
| D | 200 – 1,000 µm | 7 – 32 mm | 33 – 80 l/min |
Table 2: Dispersion covers
Different versions of the RBG system
| System | Feed rate mm/h | Reservoir diameter in mm | Reservoir length in mm | Min. mass flow | Max. mass flow |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBG 1000 | 700 | 7 - 28 | 70 | 3.8 g/h | 430 g/h |
| RBG 1000 D | 700 | 7 - 20 | 70 | 3.8 g/h | 219 g/h |
| RBG 1000 G | 300 | 7 - 28 | 70 | 3.8 g/h | 184 g/h |
| RBG 1000 GD | 300 | 7 - 20 | 70 | 3.8 g/h | 94 g/h |
| RBG 1000 L | 700 | 10, 14 | 70 | 3.8 g/h | 107 g/h |
| RBG 1000 SD | 700 | 7 - 20 | 70 | ||
| RBG 1000 SG | 300 | 7 - 20 | 70 | ||
| RBG 1000 I | 700 | 7 - 28 | 70 | ||
| RBG 1000 ID | 700 | 7 - 20 | 70 | ||
| RBG 1000 ISD | 700 | 7 - 20 | 70 | ||
| RBG 2000 | 700 | 16 - 32 | 180 | ||
| RBG 2000 D | 700 | 16, 20, 28 | 180 | ||
| RBG 2000 SD | 700 | 16, 20, 28 | 180 |
Table 3: Different versions of the RBG system
I = version for inhalation D = pressure-resistant G = low feed rate L = easily removable and weighable dosing unit S = nitrogen version.
The construction design of the RBG system allows for operation in "powder"/"no powder" pulse mode with cycle lengths ranging down to a second. The function can be set manually via the "Stop/Start" and "Forward" keys or automatically via an electric timer switch.
All RBG versions can be optionally controlled via remote control or computer.
Veröffentlichungen
- Xin, Bingying; Li Yizeh; et al.: Journal of the European Ceramic Society
- Younis, A.; Louzazni, M.; et al.: Systematic indoor experimental practices for simulating and investigating dust deposition effects on photovoltaic surfaces: A review; Energy Strategy Reviews Vol. 51
Benefits
Your special advantages
- Highest short-term and long-term dosing constancy
- Disperses virtually all non-cohesive dusts
- Easy exchange of different solid material reservoirs and dispersing covers
- Easy determination and adjustment of the mass flow
- Pulse mode
- Device easy to clean
- Quick and easy to operate
- Reliable operation
- Little maintenance required
- Reduces your operating expenses
Applications
Individual solutions for various industries
- Filter industry:
- Determination of fractional separation efficiency
- Determination of total separation efficiency
- Long-term dusting
- Filter media and ready-made filters
- Dust removal filters
- Vacuum cleaners and vacuum cleaner filters
- Car interior filters
- Engine air filters
- Calibration of particle measurement devices
- Flow visualization
- Inhalation tests
- Tracer particles for LDA, PIV, etc.
- Coating of surfaces
Technical features
In detail
- Particle size range
- 0.1 – 100 µm
- Maximum particle number concentration
- Ca. 107 particles/cm3
- Volume flow
- 0.5 – 5.0 m3/h
- Mass flow (particles)
- 0.04 – 430 g/h (with an assumed compacted density of 1 g/cm3)
- Filling height
- 70 mm
- Filling quantity
- 2.7 g (reservoir Ø = 7 mm), 5.5 g (reservoir Ø = 10 mm), 10.8 g (reservoir Ø
= 14 mm), 22 g (reservoir Ø = 20 mm), 43 g (reservoir Ø = 28 mm) - Power supply
- 115 – 230 V, 50/60 Hz
- Particle material
- Non-cohesive powders and bulks
- Dosing time
- Several hours nonstop
- Pre-pressure
- 4 – 8 bar
- Carrier/dispersion gas
- Random (generally air)
- Maximum counter pressure
- 0.2 barg
- Compressed air connection
- Quick coupling
- Feed rate
- 5 – 700 mm/h
- Reservoir inner diameter
- 7, 10, 14, 20, 28 mm
- Aerosol outlet connection
- Dispersion cover type A: Øinside= 5 mm, Øoutside = 8 mmDispersion cover type B: Øinside= 3.6 mm, Øoutside = 6 mmDispersion cover type: Øinside= 2.5 mm, Øoutside = 6 mm
- Dispersion cover
- Type A, type B, type C, type D
- Dimensions
- 465 • 320 • 200 mm (H • W • D)
- Weight
- Approx. 19 kg